Surfactant-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of flower-like tin oxide/graphene composites for high-performance supercapacitors
Abstract
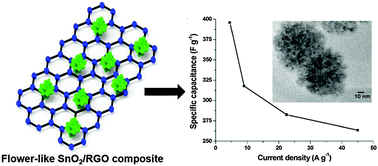
We report a simple, one-pot hydrothermal method for synthesizing tin oxide (SnO2) nanoparticle-decorated reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanocomposites. Transmission electron microscopy images show that flower-like SnO2 architectures are homogeneously dispersed onto the RGO surface. The composite exhibits a maximum specific capacitance of 396 F g−1 (at a current density of 4.5 A g−1), with a capacitance retention of 92.6% even after 10 000 continuous charge/discharge cycles, which is sevenfold higher than that of pure RGO (55 F g−1). The high capacitance is attributed to the synergetic effect of SnO2 and RGO. In addition, the composite shows efficient photodegradation of methylene blue under visible light. The enhanced degradation is ascribed to good adsorption and improved separation efficiency of photo-induced electron–hole pairs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...