Highly porous ZnO nanosheets self-assembled in rosette-like morphologies for dye-sensitized solar cell application†
Abstract
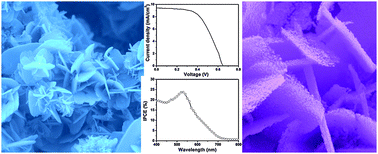
This paper reports a facile low temperature hydrothermal process to grow highly porous ZnO nanosheets, self-assembled in rosette-like morphology, over the transparent indium tin oxide (ITO) glass substrate for dye-sensitized solar cell application. The prepared porous nanosheets were examined in detail using several techniques to understand the morphological, structural, compositional, optical and photovoltaic properties. The detailed morphological investigations reveal that the prepared nanosheets are made by the accumulation of small ZnO nanoparticles with typical diameters of 28 ± 3 nm. A systematic growth process to prepare such ZnO nanosheets is also discussed in terms of chemical reactions involved. The prepared nanosheets possess the stoichiometric elemental ratios of Zn and oxygen and exhibiting good crystallinity and wurtzite hexagonal phase along with good optical properties. Furthermore, the prepared ZnO nanosheets on ITO substrates were directly utilized as a photo-anode to fabricate an efficient dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC), which demonstrated a reasonable light-to-electricity conversion efficiency of ∼3.4% with high short circuit current (JSC) of 9.45 mA cm−2, open circuit voltage (VOC) of 0.654 and fill factor of 0.55. The obtained JSC and the performance of the fabricated DSSC are attributed to the high surface to volume ratio of porous ZnO nanosheets, which delivers the high light harvesting efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...