Synthesis and mechanism of novel fluorescent coumarin–dihydropyrimidinone dyads obtained by the Biginelli multicomponent reaction†
Abstract
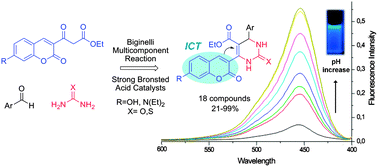
The optimization of a Biginelli Multicomponent Reaction (MCR) protocol for obtaining a collection of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one/thione, with UV absorption and blue fluorescent properties, from synthetic coumarin beta-ketoester derivatives is described. This is the first report of Biginelli adducts bearing a coumarin nucleus in the β-ketoester moiety and their MCR mechanism seems to pass through a Knoevenagel intermediate, which was considered as unlikely before. A chemical library was obtained and the dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one nucleus formation confirmed by X-ray diffraction. Photophysical analyses of representative compounds in different solvents show good Stokes shifts in water that are associated to a postulated ICT process and pKa determination make these compounds a good start point for new chemical and biological probes as well as useful pH indicators.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...