Conformational preferences in the β-peptide oligomers of cis-2-amino-1-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid†
Abstract
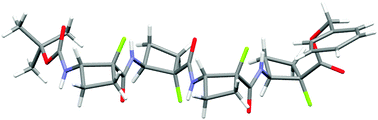
An efficient synthesis of cis-2-amino-1-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid in single enantiomer form was established and protected homo-oligomers (2-, 4-, and 6-mers) of this cyclic cis-β-amino acid were prepared. Conformational analysis of these oligomers using IR, NMR and CD techniques in solution, supported by molecular modelling studies, suggested a strong conformational preference for a well-defined strand-like structure in which intra-residue hydrogen bonding is weak at best and is not consequential for adoption of the secondary structure. Single crystal X-ray analysis of the tetramer showed that a regular strand-like conformation is adopted in the solid state; only intermolecular hydrogen bonding networks are observed. The backbone topology and the 4-membered ring orientations are noticeably different from those of the tetramer of the corresponding non-fluorinated cis-β-amino acid.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Foldamer Chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...