Hydrogen photogeneration catalyzed by a cobalt complex of a pentadentate aminopyridine-based ligand†
Abstract
A pentadentate aminopyridine ligand [(9-methyl-1,10-phenanthrolin-2-yl)methyl]bis-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine (DPA-Dmphen) has been prepared and characterized. This ligand readily accommodates Co(II) or Ni(II) bearing a coordinated apical water ligand, and the resulting complexes of general formula [M(Dmphen-DPA)(H2O)](ClO4)2 (M![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Co (1) and M
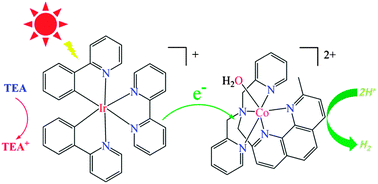
Co (1) and M![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Ni (2)) have been investigated for photo- and electrocatalytic proton reduction in CH3CN–H2O (1/3, v/v) mixed solvent and CH3CN, respectively. Under visible-light irradiation (λ > 400 nm), complex 1 shows hydrogen evolution activity in the presence of [Ir(ppy)2(bpy)]PF6 as a photosensitizer and TEA as an electron donor, whereas 2 displays much lower catalytic activity under the same conditions. The highest turnover number (TON) of 210 is achieved for H2 evolution from an optimized system containing 1 (0.1 mM), [Ir(ppy)2(bpy)](PF6) (0.5 mM), and 10 vol% TEA in CH3CN–H2O (1/3, v/v) mixed solvents at pH 10. Under those conditions catalytic hydrogen production is mainly limited by photosensitizer and catalyst stability. Furthermore, electrochemical studies reveal that both complexes are active for electrocatalytic proton reduction in acetonitrile, when using acetic acid as a proton source with overpotentials of (0.48 V vs. Fc+/Fc) for 1 and (0.46 V vs. Fc+/Fc) for 2.
Ni (2)) have been investigated for photo- and electrocatalytic proton reduction in CH3CN–H2O (1/3, v/v) mixed solvent and CH3CN, respectively. Under visible-light irradiation (λ > 400 nm), complex 1 shows hydrogen evolution activity in the presence of [Ir(ppy)2(bpy)]PF6 as a photosensitizer and TEA as an electron donor, whereas 2 displays much lower catalytic activity under the same conditions. The highest turnover number (TON) of 210 is achieved for H2 evolution from an optimized system containing 1 (0.1 mM), [Ir(ppy)2(bpy)](PF6) (0.5 mM), and 10 vol% TEA in CH3CN–H2O (1/3, v/v) mixed solvents at pH 10. Under those conditions catalytic hydrogen production is mainly limited by photosensitizer and catalyst stability. Furthermore, electrochemical studies reveal that both complexes are active for electrocatalytic proton reduction in acetonitrile, when using acetic acid as a proton source with overpotentials of (0.48 V vs. Fc+/Fc) for 1 and (0.46 V vs. Fc+/Fc) for 2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...