Synthesis of amine functionalized graphite nanosheets and their water-soluble derivative for drug loading and controlled release†
Abstract
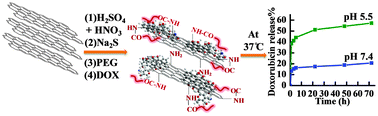
A facile route to synthesize amine (–NH2) functionalized graphite nanosheets (AFGNS) by 2-step controlled chemical modification of microcrystalline graphite is described. The method begins with nitration by mixed acid (HNO3 : H2SO4 in 1 : 1 v/v ratio), followed by reduction with Na2S to form AFGNS. The AFGNS was reacted with carboxylic acid-terminated polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains (MeO–mPEG–COOH, MW = 5000 Da) in the presence of a carbodiimide coupling agent to obtain a water-soluble PEGylated AFGNS (P-AFGNS) composite. Anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) was loaded on this composite with a loading capacity of 0.296 mg mg−1 for an initial concentration of 0.232 mg mL−1 DOX and 0.136 mg mL−1 of P-AFGNS and the release of DOX from this water-soluble DOX loaded P-AFGNS composite at two different temperatures was found to be strongly pH dependent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...