Synthesis of nano-TiO2-decorated MoS2 nanosheets for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
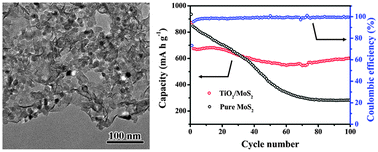
A facile process is developed to synthesize a TiO2–MoS2 nanohybrid via a one-pot hydrothermal route and post-annealing in an Ar atmosphere at 500 °C for 4 h. The precursor and target products were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). TEM and FESEM analysis showed that TiO2 nanoparticles with an average diameter of about 20 nm were uniformly distributed on MoS2 nanosheets. Electrochemical measurements demonstrated that the nano-TiO2-decorated MoS2 nanosheets exhibited excellent cycling stability and rate performance, which delivered a capacity of 604 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles at a current density of 100 mA g−1. The TiO2 is believed to act as a stabilizer to retain the MoS2 structure upon prolonged cycling. This material can be a promising candidate for the lithium ion batteries (LIBs).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...