Advances in spinel Li4Ti5O12 anode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
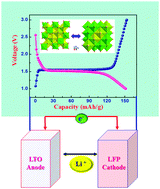
Anode materials of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries have been developed towards the aim of high power density, long cycle life, and environmental benignity. As a promising anode material for high power density batteries for large scale applications in both electric vehicle and large stationary power supplies, the spinel Li4Ti5O12 anode has become more attractive for alternative anodes for its relatively high theoretical capacity (175 mA h g−1), stable voltage plateau of 1.5 V vs. Li/Li+, better cycling performance, high safety, easy fabrication, and low cost precursors. This perspective first introduces recent studies on the electronic structure and performance, synthesis methods, and strategies for improvement including carbon-coating, ion-doping, surface modifications, nano-structuring and optimization of the particle morphology of the Li4Ti5O12 anode. Furthermore, practical applications of the commercial spinel lithium-ion batteries are demonstrated. Finally, the future research directions and key developments of the spinel Li4Ti5O12 anode are pointed out from a scientific and an industrial point of view. In addition, the prospect of the synthesis of graphene–Li4Ti5O12 hybrid composite anode materials for next-generation lithium-ion batteries is highlighted.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...