Comparative studies on OLED performances of chloro and fluoro substituted Zn(ii) 8-hydroxyquinolinates†
Abstract
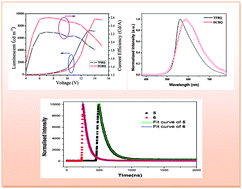
Two novel 8-hydroxyquinoline metallic derivatives, (E)-2-[(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorophenyl)ethenyl]-8-hydroxyquinolate zinc (5) and (E)-2-[2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)ethenyl]-8-hydroxyquinolate zinc (6) were synthesized and characterized by 1H NMR, ESI-MS, FT-IR and elemental analysis. Photoluminescence spectra revealed that the complexes showed strong fluorescence with maximum emissions at 575 and 607 nm. Compared with that of complex 5, the fluorescence quantum yield and average fluorescence lifetime of complex 6 were efficiently reduced. The heavy atom effect of Cl and distinct molecular interactions were found to play an important role in modulating or improving the properties of the complexes. Multilayer organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) were fabricated using these complexes. The results show they are good candidates for yellow OLEDs with maximum luminance of 7123 cd m−2 for compound 5 and 9143 cd m−2 for compound 6, as well as luminance efficiencies of 2.26 cd A−1 and 2.60 cd A−1, respectively. As the substituents are changed from fluorine to chlorine, the organic electroluminescent device based on the complex 6 shows overall better performance than that of complex 5. The calculated HOMO–LUMO energy gaps for complexes 5 and 6 were in good agreement with the experimental results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...