A dihydrogen phosphate selective anion receptor based on acylhydrazone and pyrazole†
Abstract
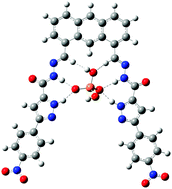
A novel chromogenic anion receptor 1 based on acylhydrazone and pyrazole has been designed and synthesized. Chromogenic anion receptor 1 forms stable 1 : 1 complexes with dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4−) and other halide (Cl−, Br−) anions in DMSO solution, as shown by UV-vis, fluorescence and 1H NMR spectroscopic experiments. The pyrazole containing host 1 in the optimized geometry of the complex has been noted as planar. The planarity of the host with the H2PO4− anion resulted from four strong N–H⋯O and two weak C–H⋯O types of H-bonding. In total six H-bonding and the planarity of the host in the complex are responsible for the high binding energy. The addition of an excess of more basic anions (F− and CH3COO−) induces stepwise deprotonation, an event signalled by the appearance of a bright yellow color. The intensity of the fluorescence spectrum increases when hydrogen bonding occurs and decreases when deprotonation occurs, which is evidenced by fluorescence titrations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...