Acetophenone derivatives: novel and potent small molecule inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B†
Abstract
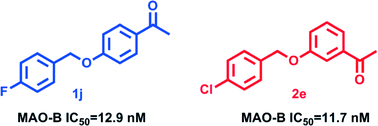
Two series of acetophenone derivatives have been designed, synthesized and evaluated for human monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitory activity in vitro. Most of the tested compounds acted preferentially on MAO-B with IC50 values in the nanomolar range and weak or no inhibition of MAO-A. In particular, compounds 1j (IC50 = 12.9 nM) and 2e (IC50 = 11.7 nM) were the most potent MAO-B inhibitors being 2.76- and 2.99-fold more active than selegiline. In addition, the structure–activity relationships for MAO-B inhibition indicated that substituents at C3 and C4 of the acetophenone moiety, particularly with the halogen substituted benzyloxy, were more favorable for MAO-B inhibition. Molecular docking and kinetic studies have been carried out to explain the binding modes of MAO-B with the acetophenone derivatives. Furthermore, the representative compounds 1j and 2e showed low neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. It may be concluded that the acetophenone derivatives could be used to develop promising lead compounds for treating neurodegenerative diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...