A metal carbonyl–protein needle composite designed for intracellular CO delivery to modulate NF-κB activity†
Abstract
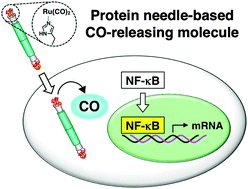
Carbon monoxide (CO) has been recognized as a messenger for signal transduction in living cells and tissues. For intracellular CO delivery, several metal carbonyl complexes have been used as CO-releasing molecules (CO-RMs). To improve the properties of CO-RMs, such as the stability and the CO release rate, ligands and carriers of the metal complexes have been exploited. Here we report the development of an efficient intracellular CO delivery system using a protein scaffold. We used a protein needle reconstructed from gene product 5 of bacteriophage T4, which has high cellular permeability and stability. When ruthenium carbonyl complexes are conjugated to the needle using a His-tag triad at the C-terminus, the resulting composite has a significantly higher cellular uptake efficiency of Ru carbonyl and a 12-fold prolonged CO release rate relative to Ru(CO)3Cl(glycinate), a widely used CO-RM. We demonstrate that CO delivered by the composite activates the transcriptional factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), which in turn leads to significant induction of expression of its target genes, HO1, NQO1, and IL6, through generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The signaling pathway is distinct from that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced activation of NF-κB. The protein needle-based CO-RM can be exploited to elucidate the biological functions of CO and used in the development of protein-based organometallic tools for modulation of cellular signaling.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...