An integrated metabolomics approach for the research of new cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of multiple sclerosis†
Abstract
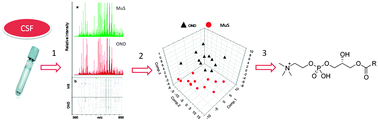
Multiple Sclerosis (MuS) is a disease caused due to an autoimmune attack against myelin components in which non proteic mediators may play a role. Recent research in metabolomics and lipidomics has been driven by rapid advances in technologies such as mass spectrometry and computational methods. They can be used to study multifactorial disorders like MuS, highlighting the effects of disease on metabolic profiling, regardless of the multiple trigger factors. We coupled MALDI-TOF-MS untargeted lipidomics and targeted LC-MS/MS analysis of acylcarnitines and aminoacids to compare cerebrospinal fluid metabolites in 13 MuS subjects and in 12 patients with Other Neurological Diseases (OND). After data processing and statistical evaluation, we found 10 metabolites that significantly (p < 0.05) segregate the two clinical groups. The most relevant result was the alteration of phospholipids levels in MuS and the correlation between some of them with clinical data. In particular lysophosphatidylcholines (m/z = 522.3 Da, 524.3 Da) and an unidentified peak at m/z = 523.0 Da correlated to the Link index, lysophosphatidylinositol (m/z = 573.3 Da) correlated to EDSS and phosphatidylinositol (m/z = 969.6 Da) correlated to disease duration. We also found high levels of glutamate in MuS. In conclusion, our integrated mass spectrometry approach showed high potentiality to find metabolic alteration in cerebrospinal fluid. These data, if confirmed in a wider clinical study, could open the door for the discovery of novel candidate biomarkers of MuS.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Proteomics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...