Comparative proteomic analyses of urine from rat urothelial carcinoma chemically induced by exposure to N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)-nitrosamine†
Abstract
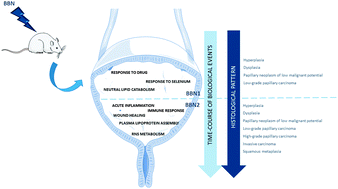
Bladder cancer is estimated to be the ninth most common malignancy with a high rate of recurrence and progression despite therapy, early diagnosis being crucial for timely intervention. Using a well-established animal model of urothelial carcinoma, we performed a comprehensive analysis of urine proteome profile from healthy animals and animals with urothelial carcinoma at two time-points of disease pathogenesis. GeLC-MS/MS, followed by bioinformatics analysis of unique proteins and the ones present in significantly distinct levels among groups, highlighted the biological processes involved in disease pathogenesis such as, for instance, response to selenium and to drugs, neutral lipid metabolism at earlier stages of disease, and inflammation, immune response and wound healing at advanced stages. Proteins from up-regulated biological processes might be seen as putative disease biomarkers. These include, for example, cadherins, lipoproteins, and glysosyltransferases, which may be included in multimarker strategies. Taken together, the data support the application of urine proteomics for the identification of the biological processes modulated by bladder cancer in an integrative perspective. The present exploratory urinary proteomic analysis might be seen as an important starting point for studies targeting urinary proteins in human, aiming at the implementation of novel laboratory approaches for the detection and successful management of urothelial carcinoma.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Proteomics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...