Integrated analysis reveals that STAT3 is central to the crosstalk between HER/ErbB receptor signaling pathways in human mammary epithelial cells†
Abstract
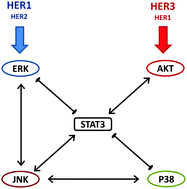
Human epidermal growth factor receptors (HER, also known as ErbB) drive cellular proliferation, pro-survival and stress responses by activating several downstream kinases, in particular ERK, p38 MAPK, JNK (SAPK), the PI3K/AKT, as well as various transcriptional regulators such as STAT3. When co-expressed, the first three members of HER family (HER1–3) can form homo- and hetero-dimers, and there is considerable evidence suggesting that the receptor dimers differentially activate intracellular signaling pathways. To better understand the interactions in this system, we pursued multi-factorial experiments where HER dimerization patterns and signaling pathways were rationally perturbed. We measured the activation of HER1–3 receptors and of the sentinel signaling proteins ERK, AKT, p38 MAPK, JNK, STAT3 as a function of time in a panel of human mammary epithelial (HME) cells expressing different levels of HER1–3 stimulated with various ligand combinations. We hypothesized that the HER dimerization pattern is a better predictor of downstream signaling than the total receptor activation levels. We validated this hypothesis using a combination of model-based analysis to quantify the HER dimerization patterns, and by clustering the activation data in multiple ways to confirm that the HER receptor dimer is a better predictor of the signaling through p38 MAPK, ERK and AKT pathways than the total HER receptor expression and activation levels. We then pursued combinatorial inhibition studies to identify the causal regulatory interactions between sentinel signaling proteins. Quantitative analysis of the collected data using the modular response analysis (MRA) and its Bayesian Variable Selection Algorithm (BVSA) version allowed us to obtain a consensus regulatory interaction model, which revealed that STAT3 occupies a central role in the crosstalk between the studied pathways in HME cells. Results of the BVSA/MRA and cluster analysis were in agreement with each other.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...