The effect of hydride formation on instrumental mass discrimination in MC-ICP-MS: a case study of mercury (Hg) and thallium (Tl) isotopes
Abstract
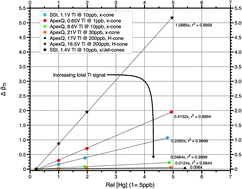
Here we report evidence for enhanced hydride formation for Hg isotopes when using high sensitivity X skimmer cones and the Neptune MC-ICP-MS. The effect on the instrumental mass discrimination and the robustness of the Tl external mass-bias correction was investigated. A series of experiments have been conducted to study the effect of variable Hg concentrations on the measured mass bias correction factor, βTl. The results of our experiments show a linear relation between the Hg concentration and the measured 205Tl/203Tl ratio of the internal standard. The resulting mass-bias correction factor βTl thus appears to be dependent on the analyte concentration, questioning the applicability of Tl as an internal standard for high precision Hg isotope ratio measurements. These observations are consistent with the formation of Hg hydrides (HgHx where x = 1, 2). Numerical simulations show Hg hydride formation rates of 0.02 to 0.18% to be consistent with experimental observations, when using high-sensitivity X skimmer cones. Here we discuss the implications of Hg hydride formation for Hg isotope ratio measurements and propose a set of precautionary steps that can help to identify and remediate analytical issues related to hydride formation. Whilst the effect of hydride formation on mass-dependent Hg isotope ratios can be controlled, mass independent Hg ratios are shown to be very sensitive to hydride formation. A comparison between different types of sediment samples and standards also suggests a matrix dependency on hydride formation. We conclude that precise and accurate Hg isotope ratio determination using MC-ICP-MS is possible, however, probably not to low ppm-levels of precision.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...