Efficient testosterone production by engineered Pichia pastoris co-expressing human 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase with NADPH regeneration†
Abstract
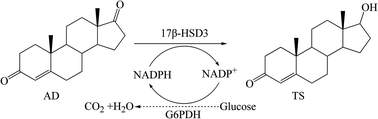
Traditionally, testosterone (TS), an important hormone drug and precursor for the synthesis of other steroids, was chemically produced. Recently, TS has been prepared through side-chain degradation of some sterols (cholesterol or phytosterol) using microbial fermentation methods. However, the TS production is at a low level, and the biotransformation process is long and with many by-products formed. NADPH-dependent 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 (17β-HSD3) from human testis catalyzes the conversion of 4-androstene-3,17-dione (AD) to TS. In this work, we optimized the gene codons of human 17β-HSD3 and realized its functional expression in Pichia pastoris GS115. The engineered P. pastoris/17β-HSD3 cells exhibited good selectivity for the efficient transformation of AD to TS. Moreover, Saccharomyces cerevisiae glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) was introduced to strengthen the NADPH regeneration system into the pathway from AD to TS by P. pastoris/17β-HSD3. By optimization of the transformation conditions from AD to TS and applying the fed-batch strategy, the co-expressed system P. pastoris/17β-HSD3-G6PDH produced TS of 11.6 g L−1, which is the highest reported yield using a bioconversion method. Compared with the ever highest reported production (≤1.7 g L−1), our production was improved by about 7-fold. More importantly, no by-products were detected during the whole bioconversion process. This study indicated that the recombinant P. pastoris harboring 17β-HSD3 and G6PDH could be a promising candidate to produce TS in the pharmaceutical industry. The P. pastoris system co-expression target enzyme and the cofactor regeneration enzyme may be helpful for enhancing the production of other steroids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...