Hexamethylenediamine (HMDA) from fossil- vs. bio-based routes: an economic and life cycle assessment comparative study†
Abstract
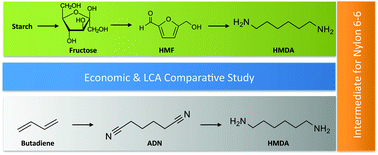
Hexamethylenediamine (HMDA) is one of the key intermediates in the preparation of nylon 6-6 by polycondensation with adipic acid. Currently, the most used commercial process for HMDA manufacture proceeds via the hydrogenation of adiponitrile in ammonia, which is in turn produced by the hydrocyanation of butadiene. In this paper, we explore three alternative bio-based paths for HMDA production starting from high fructose syrup made from maize and potato-derived starch and using 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural (HMF) as intermediate building block. Different routes have been compared using a combined economic and life-cycle assessment study including a sensitivity analysis on potential key parameters. Overall, our study reflects a higher economic benefit and a lower environmental impact of the benchmark fossil-based route. As for the environmental impact, the most advantageous of the three bio-based routes could present benefits in terms of CO2 footprint when the carbon sink is taken into account, but at the expense of a higher impact on terrestrial, marine and freshwater eutrophication. Possible process improvements to make bio-based routes affordable for HMDA production are proposed as an attempt to draw general rules for process eco-design.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...