Direct synthesis of 2-ethylhexanol via n-butanal aldol condensation–hydrogenation reaction integration over a Ni/Ce-Al2O3 bifunctional catalyst†
Abstract
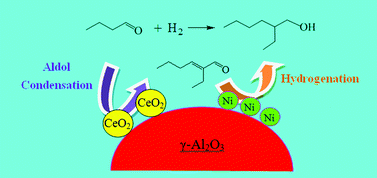
Direct synthesis of 2-ethylhexanol from n-butanal via the reaction integration of n-butanal self-condensation with 2-ethyl-2-hexenal hydrogenation is of crucial interest for industrial production of 2-ethylhexanol. Furthermore, as an important and versatile chemical, n-butanol can be produced simultaneously by reaction integration. In the present work, several bifunctional catalysts based on γ-Al2O3 were prepared by the impregnation method and were characterized by means of H2-TPR, XRD, TEM and H2-TPD, and their catalytic performance for direct synthesis of 2-ethylhexanol from n-butanal was investigated. The results showed that Co/Al2O3 had a low activity for hydrogenation and Cu/Al2O3 had a high selectivity for the hydrogenation of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group while a Ru/Al2O3 catalyst only favored the hydrogenation of n-butanal to n-butanol. Among them, the Ni/Al2O3 catalyst showed the best catalytic performance and the yield of 2-ethylhexanol was the highest (49.4%). Ce-modified Ni/Al2O3 enhanced the competitiveness of aldol condensation versus hydrogenation of n-butanal and improved the selectivity of 2-ethylhexanol; the yield of 2-ethylhexanol rose to 57.8%. Then the influence of preparation conditions on the catalytic performance of Ni/Ce-Al2O3 was investigated and the suitable preparation conditions were obtained as follows: Ni loading = 10%, calcined at 550 °C for 5 h, and reduced at 570 °C for 4 h. The effect of reaction conditions on the integration reaction catalyzed by Ni/Ce-Al2O3 was investigated and the suitable reaction conditions were obtained as follows: weight percentage of Ni/Ce-Al2O3 = 15%, reaction temperature = 170 °C, reaction pressure = 4.0 MPa and reaction time = 8 h. Under the above reaction conditions, the yield of 2-ethylhexanol attained 66.9% and that of n-butanol was 18.9%. In addition, the components existing in the integration reaction system were identified by GC-MS analysis, and the main by-products were n-butyl butyrate, 2-ethylhexyl butyrate, n-butyric acid, etc. Based on the analysis of the reaction system, a reaction network for the direct synthesis of 2-ethylhexanol from n-butanal was proposed. Finally, an evaluation of the reusability of Ni/Ce-Al2O3 showed that the recovered Ni/Ce-Al2O3 catalyst lost its catalytic activity for the hydrogenation of the C
O group while a Ru/Al2O3 catalyst only favored the hydrogenation of n-butanal to n-butanol. Among them, the Ni/Al2O3 catalyst showed the best catalytic performance and the yield of 2-ethylhexanol was the highest (49.4%). Ce-modified Ni/Al2O3 enhanced the competitiveness of aldol condensation versus hydrogenation of n-butanal and improved the selectivity of 2-ethylhexanol; the yield of 2-ethylhexanol rose to 57.8%. Then the influence of preparation conditions on the catalytic performance of Ni/Ce-Al2O3 was investigated and the suitable preparation conditions were obtained as follows: Ni loading = 10%, calcined at 550 °C for 5 h, and reduced at 570 °C for 4 h. The effect of reaction conditions on the integration reaction catalyzed by Ni/Ce-Al2O3 was investigated and the suitable reaction conditions were obtained as follows: weight percentage of Ni/Ce-Al2O3 = 15%, reaction temperature = 170 °C, reaction pressure = 4.0 MPa and reaction time = 8 h. Under the above reaction conditions, the yield of 2-ethylhexanol attained 66.9% and that of n-butanol was 18.9%. In addition, the components existing in the integration reaction system were identified by GC-MS analysis, and the main by-products were n-butyl butyrate, 2-ethylhexyl butyrate, n-butyric acid, etc. Based on the analysis of the reaction system, a reaction network for the direct synthesis of 2-ethylhexanol from n-butanal was proposed. Finally, an evaluation of the reusability of Ni/Ce-Al2O3 showed that the recovered Ni/Ce-Al2O3 catalyst lost its catalytic activity for the hydrogenation of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group. The main reason for deactivation was that Ni species were covered by the flaky boehmite γ-AlO(OH) formed from the hydration of γ-Al2O3 in the reaction process.
O group. The main reason for deactivation was that Ni species were covered by the flaky boehmite γ-AlO(OH) formed from the hydration of γ-Al2O3 in the reaction process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...