Synthesis of biomass-derived methylcyclopentane as a gasoline additive via aldol condensation/hydrodeoxygenation of 2,5-hexanedione†
Abstract
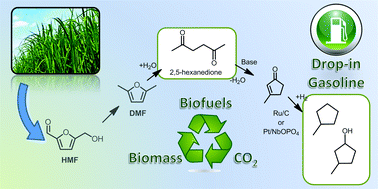
A novel approach to produce biomass-derived gasoline is the hydrolysis of 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF) to produce 2,5-hexanedione followed by base-catalyzed intramolecular aldol condensation of this product to form 3-methylcyclopent-2-enone (MCP). By proper choice of catalysts and conditions, MCP yields of 98% can be achieved. We further show that hydrogenation of MCP over Pt/NbOPO4 gives methylcyclopentane with virtually quantitative yields. Methylcyclopentane is an attractive gasoline substitute for ethanol, since its octane number is similar to ethanol and its gravimetric energy density is 58% higher.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...