Protective effects of germinated and fermented soybean extract against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells and in rats
Abstract
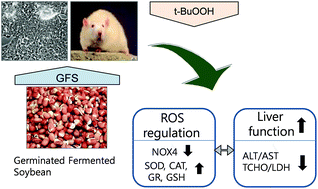
The aim of the current study is to investigate the antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of germinated and fermented soybean extract (GFSE) on tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells and in the rat liver. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis showed that genistin (3.40 ± 0.14 μg mg−1) was the most abundant isoflavone in the GFSE. Coumestrol (1.00 ± 0.04 μg mg−1), daidzin (0.78 ± 0.14 μg mg−1), genistein (0.68 ± 0.05 μg mg−1), glycitin (0.54 ± 0.02 μg mg−1), glycitein (0.41 ± 0.02 μg mg−1), and daidzein (0.02 ± 0.0 g mg−1) are also contained in decreasing order of content. GFSE significantly inhibited t-BHP-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in HepG2 cells. This GFSE-induced ROS reduction was associated with the down-regulation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 (NOX4), a pro-oxidant enzyme, and the up-regulation of the mRNA levels of antioxidant enzymes, including catalase, superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione reductase (GR), and glutathione peroxidase (Gpx) in the rat liver. In addition, increased levels of antioxidant enzyme mRNAs correlated with the enhanced enzymatic activities of SOD, catalase, and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). The antioxidant effect of GFSE was supported by the reduction in the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a hydroperoxide, and the serum levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a biomarker of cell damage, were also lowered by GFSE. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are clinical biomarkers of liver function, were shown to be improved with GFSE administration. The effects of GFSE were attributable to an improvement in liver tissue morphology. Taken together, GFSE protected the liver from t-BHP-induced oxidative stress by regulating ROS-related enzymes. Our results suggest that GFSE might be a hepatoprotective source against oxidative stress.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...