Effects of edible bird's nest on hippocampal and cortical neurodegeneration in ovariectomized rats
Abstract
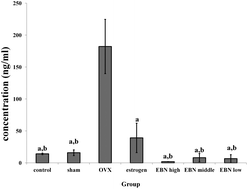
The aim of this research is to investigate whether edible bird's nest (EBN) attenuates cortical and hippocampal neurodegeneration in ovariectomized rats. Ovariectomized rats were randomly divided into seven experimental groups (n = 6): the ovariectomy (OVX) group had their ovaries surgically removed; the sham group underwent surgical procedure similar to OVX group, but ovaries were left intact; estrogen group had OVX and received estrogen therapy (0.2 mg kg−1 per day); EBN treatment groups received 6%, 3%, and 1.5% EBN, respectively. Control group was not ovariectomized. After 12 weeks of intervention, biochemical assays were performed for markers of neurodegeneration, and messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) levels of oxidative stress-related genes in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of the brain were analysed. Caspase 3 (cysteine-aspartic proteases 3) protein levels in the hippocampus and frontal cortex were also determined using western blotting. The results show that EBNs significantly decreased estrogen deficiency-associated serum elevation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), and they changed redox status as evidenced by oxidative damage (malondialdehyde content) and enzymatic antioxidant defense (superoxide dismutase and catalase) markers. Furthermore, genes associated with neurodegeneration and apoptosis were downregulated in the hippocampus and frontal cortex by EBN supplementation. Taken together, the results suggest that EBN has potential for neuroprotection against estrogen deficiency-associated senescence, at least in part via modification of the redox system and attenuation of AGEs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Alzheimer's Research Month 2016


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...