The effect of quercetin and kaempferol aglycones and glucuronides on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ)
Abstract
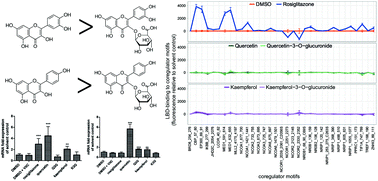
The consumption of dietary flavonoids has been associated with a variety of health benefits, including effects mediated by the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ). Flavonoids are extensively metabolized during and after uptake and there is little known on the biological effects of these conjugated metabolites of flavonoids that are found in plasma. To investigate the effect of glucuronidation on the ability of flavonoids to activate PPAR-γ we studied and compared the activity of quercetin, kaempferol and their relevant plasma conjugates quercetin-3-O-glucuronide (Q3G) and kaempferol-3-O-glucuronide (K3G) on different PPAR-γ related endpoints. The flavonoid aglycones increased PPAR-γ mediated gene expression in a stably transfected reporter gene cell line and glucuronidation diminished their effect. To study the intrinsic activity of the test compounds to activate PPAR-γ we used a novel microarray technique to study ligand induced ligand binding domain (LBD) – nuclear receptor coregulator interactions. In this cell-free system we demonstrate that, unlike the known PPAR-γ agonist rosiglitazone, neither the flavonoid aglycones nor the conjugates are agonistic ligands of the receptor. The increases in reporter gene expression in the reporter cells were accompanied by increased PPAR-γ receptor-mRNA expression and quercetin synergistically increased the effect of rosiglitazone in the reporter gene assay. It is concluded that flavonoids affect PPAR-γ mediated gene transcription by a mode of action different from agonist binding. Increases in PPAR-γ receptor mRNA expression and synergistic effects with endogenous PPAR-γ agonists may play a role in this alternative mode of action. Glucuronidation reduced the activity of the flavonoid aglycones.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...