Antiproliferative effect of Dendrobium catenatum Lindley polypeptides against human liver, gastric and breast cancer cell lines†
Abstract
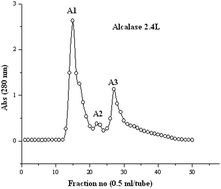
Dendrobium catenatum Lindley is a precious plant with both dietary and medicinal applications. However, the antiproliferative activity of D. catenatum-derived peptides has not been investigated. In this study, the whole proteins of D. catenatum were extracted, hydrolysis with three proteases (alcalase 2.4L, alcalase 37017 and trypsin) was performed, and gel filtration chromatography was employed to obtain nine fractions. Fraction A3 possessed the best antiproliferative activity in vitro, with percentage inhibitions of 73.38%, 78.91% and 86.8% against HepG-2, SGC-7901 and MCF-7 cancer cells, respectively, and an inhibition of only 5.52% against L-O2 normal liver cells at 500 μg mL−1. Subsequently, mass spectrometry revealed the existence of 10 alcalase-derived peptides in fraction A3, and the sequences of the three most abundant peptides were determined by de novo sequencing as: RHPFDGPLLPPGD, RCGVNAFLPKSYLVHFGWKLLFHFD and KPEEVGGAGDRWTC. Moreover, these peptides were synthesized and their antiproliferative activities in vitro were also confirmed. This suggests that fraction A3 may be promising for use in food and pharmaceutical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...