Bioaccessibility of polyphenols associated with dietary fiber and in vitro kinetics release of polyphenols in Mexican ‘Ataulfo’ mango (Mangifera indica L.) by-products
Abstract
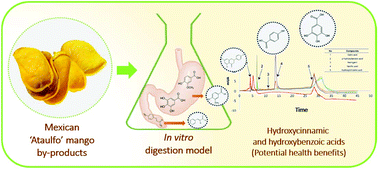
The biological properties of polyphenol (PP) depend on its bioaccessibility and bioavailability. Therefore, part of PP released from the food matrix in the gastrointestinal tract through enzymatic hydrolysis is at least partially absorbed. The aim of this study is to determine the bioaccessibility of PP associated with dietary fiber (DF) and the kinetics release of PP in mango (Mangifera indica L.) ‘Ataulfo’ by-products by an in vitro model. Soluble and insoluble DF values were 7.99 and 18.56% in the mango paste and 6.98 and 22.78% in the mango peel, respectively. PP associated with soluble and insoluble DF was 6.0 and 3.73 g GAE per 100 g in the paste and 4.72 and 4.50 g GAE per 100 g in the peel. The bioaccessibility of PP was 38.67% in the pulp paste and 40.53% in the peel. A kinetics study shows a release rate of 2.66 and 3.27 g PP min−1 in the paste and peel, respectively. The antioxidant capacity of the paste increased as digestion reached a value of 2.87 mmol TE min−1 at 180 min. The antioxidant capacity of the peel had its maximum (28.94 mmol TE min−1) between 90 and 120 min of digestion; it started with a value of 2.58 mmol TE min−1, and thereafter increased to 4.20 mmol TE min−1 at 180 min. The major PPs released during the digestion of paste were gallic and hydroxybenzoic acids, while in the peel, they were hydroxycinnamic and vanillic acids. It was concluded that these phenolic compounds are readily available for absorption in the small intestine and exert different potential health benefits.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...