River transport of mercury from artisanal and small-scale gold mining and risks for dietary mercury exposure in Madre de Dios, Peru†
Abstract
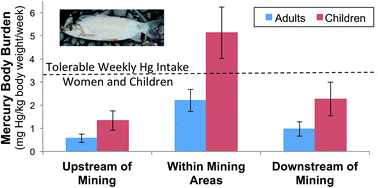
Artisanal and small-scale gold mining (ASGM) is a major contributor to deforestation and the largest anthropogenic source of atmospheric mercury worldwide. Despite significant information on the direct health impacts of mercury to ASGM miners, the impact of mercury contamination on downstream communities has not been well characterized, particularly in Peru's Madre de Dios region. In this area, ASGM has increased significantly since 2000 and has led to substantial political and social controversy. This research examined the spatial distribution and transport of mercury through the Madre de Dios River with distance from ASGM activity. This study also characterized risks for dietary mercury exposure to local residents who depend on fish from the river. River sediment, suspended solids from the water column, and fish samples were collected in 2013 at 62 sites near 17 communities over a 560 km stretch of the Madre de Dios River and its major tributaries. In areas downstream of known ASGM activity, mercury concentrations in sediment, suspended solids, and fish within the Madre de Dios River were elevated relative to locations upstream of mining. Fish tissue mercury concentrations were observed at levels representing a public health threat, with greater than one-third of carnivorous fish exceeding the international health standard of 0.5 mg kg−1. This study demonstrates that communities located hundreds of kilometers downstream of ASGM activity, including children and indigenous populations who may not be involved in mining, are at risk of dietary mercury exposure that exceed acceptable body burdens. This report represents the first systematic study of the region to aid policy decision-making related to ASGM activities in Peru.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...