Rare-earth metal π-complexes of reduced arenes, alkenes, and alkynes: bonding, electronic structure, and comparison with actinides and other electropositive metals
Abstract
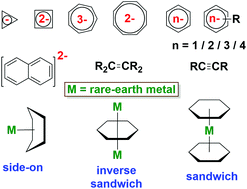
Rare-earth metal complexes of reduced π ligands are reviewed with an emphasis on their electronic structure and bonding interactions. This perspective discusses reduced carbocyclic and acyclic π ligands; in certain categories, when no example of a rare-earth metal complex is available, a closely related actinide analogue is discussed. In general, rare-earth metals have a lower tendency to form covalent interactions with π ligands compared to actinides, mainly uranium. Despite predominant ionic interactions in rare-earth chemistry, covalent bonds can be formed with reduced carbocyclic ligands, especially multiply reduced arenes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...