Targeted water soluble copper–tetrazolate complexes: interactions with biomolecules and catecholase like activities†
Abstract
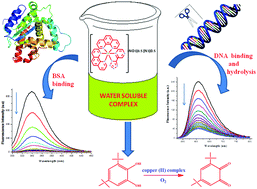
Two new mononuclear water soluble copper(II) complexes, [Cu{(5-pyrazinyl)tetrazolate}2(1,10-phenanthroline)] 1 and [Cu{(5-pyrazinyl)tetrazolate}(1,10-phenanthroline)2](NO3)0.5(N3)0.52, have been synthesized using the metal mediated [2 + 3] cycloaddition reaction between copper bound azide and pyrazinecarbonitrile. The interactions of these copper tetrazolate complexes 1 and 2 with biomolecules like DNA and bovine serum albumin (BSA) are studied and the catecholase like catalytic activity of compound 2 is also explored. Structural determination reveals that both compounds 1 and 2 are octahedral in nature. Screening tests were conducted to quantify the binding ability of complexes (1 and 2) towards DNA and it was revealed that complex 2 has a stronger affinity to bind to CT-DNA. DFT studies indicated that a lower HOMO–LUMO energy gap between the DNA fragment and metal complexes might be the reason for this type of stronger interaction. DNA cleavage activity was explored by gel-electrophoresis and moderate to strong DNA cleavage properties were observed in the presence and absence of co-reagents. Inhibition of cleavage in the presence of sodium azide indicates the propagation of the activity through the production of singlet molecular oxygen. Furthermore enzyme kinetic studies reflect that complex 2 is also effective in mimicking catecholase like activities. An ESI-MS spectral study indicates the probable involvement of dimeric species [(phen)2Cu-(OH)2-Cu(phen)2]2+ in the catalytic cycle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...