Composition–solubility–structure relationships in calcium (alkali) aluminosilicate hydrate (C-(N,K-)A-S-H)†
Abstract
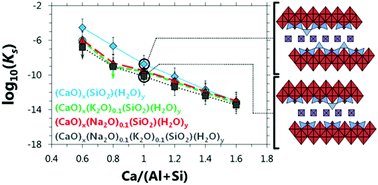
The interplay between the solubility, structure and chemical composition of calcium (alkali) aluminosilicate hydrate (C-(N,K-)A-S-H) equilibrated at 50 °C is investigated in this paper. The tobermorite-like C-(N,K-)A-S-H products are more crystalline in the presence of alkalis, and generally have larger basal spacings at lower Ca/Si ratios. Both Na and K are incorporated into the interlayer space of the C-(N,K-)A-S-H phases, with more alkali uptake observed at higher alkali and lower Ca content. No relationship between Al and alkali uptake is identified at the Al concentrations investigated (Al/Si ≤ 0.1). More stable C-(N,K-)A-S-H is formed at higher alkali content, but this factor is only significant in some samples with Ca/Si ratios ≤1. Shorter chain lengths are formed at higher alkali and Ca content, and cross-linking between (alumino)silicate chains in the tobermorite-like structure is greatly promoted by increasing alkali and Al concentrations. The calculated solubility products do not depend greatly on the mean chain length in C-(N,K-)A-S-H at a constant Ca/(Al + Si) ratio, or the Al/Si ratio in C-(N,K-)A-S-H. These results are important for understanding the chemical stability of C-(N,K-)A-S-H, which is a key phase formed in the majority of cements and concretes used worldwide.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...