Structural and electronic characterization of multi-electron reduced naphthalene (BIAN) cobaloximes†
Abstract
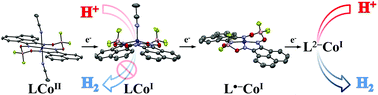
Reported here are the syntheses and characterization of cobaloximes that feature a bis(imino)acenaphthene (BIAN) appended ligand. The X-ray crystal structures and spectroscopy (1H NMR or EPR) of the complexes within the series [Co(aqdBF2)2(MeCN)2] (1), [Co(aqdBF2)(MeCN)2]− (2) and [Co(aqdBF2)2(MeCN)2]2− (3, 3′) are reported and the 3-electron reduced complex [Co(aqdBF2)2(MeCN)2]3− (4) has been prepared in situ and characterized by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The X-ray crystal structures revealed the presence of a 6-coordinate CoII species (1), a 5-coordinate CoI species (2), and a 4-coordinate complex (3, 3′). In the case of complex 3, evidence from single crystal EPR spectroscopy (g‖ = 2.017, g⊥ = 1.987; <10 G linewidths) in conjunction with DFT calculations indicate that the EPR signal originates from a delocalized ligand-based unpaired spin. The frontier orbitals obtained from DFT calculations on 1, 2, 3, & 4 support the electronic assignments that were observed spectroscopically. The cathodic cyclic voltammogram (CV) of the solvato congener in DMF solution, namely [Co(aqdBF2)2(DMF)2], exhibits three reversible redox events near −1.0, −1.5 and −2.0 V vs. Fc/Fc+. Catalytic proton reduction was observed by CV near the third redox peak. Compared with other cobaloximes (Ecat = −1.0 V), the delay of catalytic onset arises from the existence of a series of resonance-stabilized intermediates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...