Synthesis of alloy AuCu nanoparticles with the L10 structure in an ionic liquid using sputter deposition
Abstract
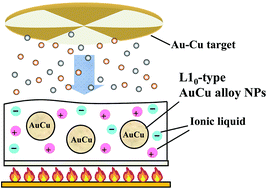
Sputter deposition onto ionic liquids (ILs) was applied to synthesize AuCu bimetallic alloy nanoparticles (NPs) dispersed in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMI-BF4). A mixed target of Au and Cu materials was used for simultaneous sputter deposition onto the IL under an Ar pressure of 10 Pa. Two types of heating procedures within the range of 323–573 K were examined for control of the structures of NPs, particularly addressing the phase transition of the alloy NPs from the face centered cubic (fcc) structure to the L10 structure. One was heating after the sputter deposition in N2 at atmospheric pressure for 1 h. Another was a combination of heating during the sputter deposition and subsequent heating under an Ar pressure from 0.5 to 0.8 Pa for 1 h. Although both cases exhibited lowering of the phase transition temperatures compared with the temperature for the bulk, the latter procedure at 423 K only provided the NPs (approx. 5 nm) consisting of the L10 structure in the dispersed manner. A mechanism for forming the L10 structure was proposed for explaining the difference between results obtained using the two procedures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...