Iron catalyzed halogenation of benzylic aldehydes and ketones†
Abstract
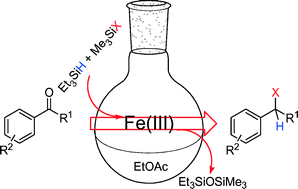
A simple and efficient iron-catalyzed method for chlorination of aromatic carbonyl compounds is reported. By using 4–10 mol% Fe(III) oxo acetate catalyst, prepared by solid state atmospheric oxidation of Fe(II) acetate, in combination with triethylsilane and chlorotrimethylsilane, hydrosilylation of benzylic carbonyl compounds with subsequent chlorination is achieved within a few hours at room temperature. This new method is mild and rapid compared to the conventional two step approach involving reduction and chlorination reactions in separate stages. Development of synthetic methodology is also supplemented here by kinetic investigation of the reaction mechanism, which supports the tentative mechanisms suggested previously for similar reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...