High surface area La2Sn2O7 pyrochlore as a novel, active and stable support for Pd for CO oxidation
Abstract
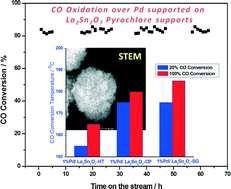
A high surface area mesoporous La2Sn2O7 compound with a well crystallized pyrochlore structure has been successfully prepared by a simple low temperature hydrothermal (La2Sn2O7-HT) method. As a support for Pd, a catalyst with a significantly higher activity for CO oxidation has been achieved in comparison with the other two non-mesoporous pyrochlores prepared by co-precipitation (La2Sn2O7-CP) and sol–gel (La2Sn2O7-SG) methods. The CO adsorption–desorption and STEM results demonstrate that on Pd/La2Sn2O7-HT, the highest Pd dispersion can be achieved among all of the catalysts. Moreover, compared with Pd/La2Sn2O7-CP and Pd/La2Sn2O7-SG, more active oxygen species were formed on Pd/La2Sn2O7-HT. It is believed that these are the two major reasons accounting for the superior CO oxidation activity of Pd/La2Sn2O7-HT. Furthermore, this catalyst also shows a stable reaction performance in the presence of water vapour. In conclusion, the mesoporous La2Sn2O7-HT pyrochlore is an excellent support for Pd, and has the potential to be applied in some real exhaust control processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...