Controlled synthesis of Pd–NiO@SiO2 mesoporous core–shell nanoparticles and their enhanced catalytic performance for p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation with H2†
Abstract
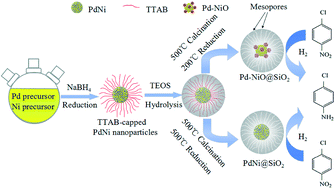
In this work, Pd–NiO@SiO2 core–shell mesoporous nanocatalysts with ~4 nm Pd–NiO heteroaggregate nanoparticle cores and ~17 nm mesoporous silica shells were successfully synthesized by a sol–gel method. The surfactant-capped PdNi alloy nanoparticles were coated with SiO2 through hydrolysis of tetraethylorthosilicate to obtain PdNi@SiO2 nanoparticles, and the mesoporous Pd–NiO@SiO2 core–shell nanocatalysts were formed after removal of surfactants by calcination at 500 °C and subsequent H2 reduction at 200 °C. The characterization results by XRD, TEM and BET revealed that Pd–NiO@SiO2 nanocatalysts were highly stable with the maintenance of intact core–shell structures under high-temperature thermal treatments. The Pd–NiO@SiO2 nanocatalysts illustrated a superior catalytic performance for p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation with H2 to the control Pd@SiO2 nanocatalysts. The catalytic performance enhancement of Pd–NiO@SiO2 nanocatalysts is ascribed to the strong interaction between Pd and NiO in the cores, where the interfaces may be beneficial for hydrogenation reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...