Conformational changes in the heat-induced crystallization of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) in the solid state†
Abstract
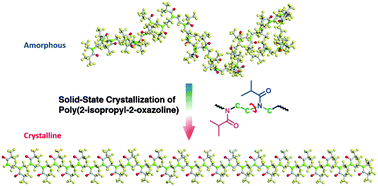
Poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) (PIPOZ) with an isomeric structure of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) represents an important class of stimuli-responsive synthetic polymers. Unlike PNIPAM, PIPOZ exhibits an unusual heat-induced crystallization behaviour at around 120 °C in the solid state, whose dynamic mechanism involving all group motions and conformational changes is still poorly understood. In this paper, IR spectroscopy in combination with two-dimensional analysis methods – the perturbation correlation moving window (PCMW) and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (2DCOS) – was used to monitor and study the conformational changes in the crystallization of PIPOZ in the solid state. The incorporated water molecules are found to be not necessary to assist the solid-state crystallization of the PIPOZ film. PCMW and 2DCOS analyses reveal that following the breaking of minor CH3⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C hydrogen bonds, all the group moieties exhibit highly synergetic motions during crystallization, and methylene groups on the backbone do not show significant changes throughout the crystallization process. Raman spectroscopic and molecular dynamics simulation results further support this conclusion. The chain alignment of PIPOZ chains is shown to be mainly achieved by the lateral distortion of coplanar side chains or the ordered chain arrangement of amide dipoles together with the torsion of the backbone through C–N linkages. Upon heating, gauche conformations of methylene groups on the backbone are always dominating, resulting in an ordered PIPOZ chain with alternate side chains and a slightly distorted backbone.
C hydrogen bonds, all the group moieties exhibit highly synergetic motions during crystallization, and methylene groups on the backbone do not show significant changes throughout the crystallization process. Raman spectroscopic and molecular dynamics simulation results further support this conclusion. The chain alignment of PIPOZ chains is shown to be mainly achieved by the lateral distortion of coplanar side chains or the ordered chain arrangement of amide dipoles together with the torsion of the backbone through C–N linkages. Upon heating, gauche conformations of methylene groups on the backbone are always dominating, resulting in an ordered PIPOZ chain with alternate side chains and a slightly distorted backbone.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...