Picosecond melting of peptide nanotubes using an infrared laser: a nonequilibrium simulation study†
Abstract
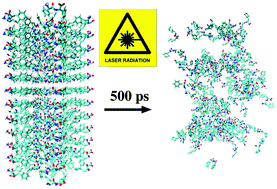
Self-assembled functional peptide biomaterials are emerging with a wide range of envisioned applications in the field of nanotechnology. Currently, methods and tools have been developed to control and manipulate as well as to explore new properties of self-assembled structures. However, considerably fewer studies are being devoted to developing efficient methods to degrade or recycle such extremely stable biomaterials. With this in mind, here we suggest a theoretical framework, inspired by the recent developed mid-infrared free-electron laser pulse technology, to dissociate peptide nanotubes. Adopting a diphenylalanine channel as a prototypical example, we find that the primary step in the dissociation process occurs due to the strong resonance between the carboxylate bond vibrations of the diphenylalanine peptides and the tuned laser frequencies. The effects of laser irradiation are determined by a balance between tube formation and dissociation. Our work shows a proof of concept and should provide a motivation for future experimental developments with the final aim to open a new and efficient way to cleave or to recycle bio-inspired materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...