Formation and nitrile hydrogenation performance of Ru nanoparticles on a K-doped Al2O3 surface†
Abstract
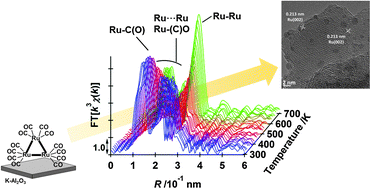
Decarbonylation-promoted Ru nanoparticle formation from Ru3(CO)12 on a basic K-doped Al2O3 surface was investigated by in situ FT-IR and in situ XAFS. Supported Ru3(CO)12 clusters on K-doped Al2O3 were converted stepwise to Ru nanoparticles, which catalyzed the selective hydrogenation of nitriles to the corresponding primary amines via initial decarbonylation, the nucleation of the Ru cluster core, and the growth of metallic Ru nanoparticles on the surface. As a result, small Ru nanoparticles, with an average diameter of less than 2 nm, were formed on the support and acted as efficient catalysts for nitrile hydrogenation at 343 K under hydrogen at atmospheric pressure. The structure and catalytic performance of Ru catalysts depended strongly on the type of oxide support, and the K-doped Al2O3 support acted as a good oxide for the selective nitrile hydrogenation without basic additives like ammonia. The activation of nitriles on the modelled Ru catalyst was also investigated by DFT calculations, and the adsorption structure of a nitrene-like intermediate, which was favourable for high primary amine selectivity, was the most stable structure on Ru compared with other intermediate structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...