SnO2(β-Bi2O3)/Bi2Sn2O7 nanohybrids doped with Pt and Pd nanoparticles: applications in visible light photocatalysis, electrical conductivity and dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
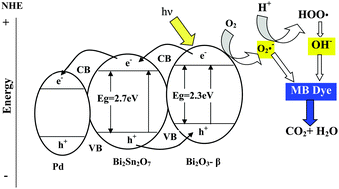
Bi2O3–SnO2 nanocomposites formed at a nominal molar ratio of 3 : 1 and loaded with Pd/Pt nanoparticles synthesized by a sol gel-hydrothermal method with the aid of a template were thoroughly characterized by X-ray diffraction, TEM-EDX, N2 sorptiometry, diffuse reflectance UV-Vis, FTIR, photoluminescence and electrical conductivity. It has been shown that Pd and Pt stimulate the existence of β-Bi2O3 and SnO2, respectively together with the key component Bi2Sn2O7. The photocatalytic results indicate that Pd/β-Bi2O3–Bi2Sn2O7 revealed a remarkable performance for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) dye as compared to the Pt/SnO2–Bi2Sn2O7 and Bi2O3–SnO2 samples in both the UV and visible regions. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of the Pd/β-Bi2O3–Bi2Sn2O7 nanocomposite is primarily attributed to the broad contact between the β-Bi2O3 and Bi2Sn2O7 phases, which indicates high mesoporosity and heterojunction structures resulting in separation efficacy between photo-induced electron–hole pairs. Specifically, the photosensitive β-Bi2O3 is easily excited and released electrons to be accepted by Bi2Sn2O7 and Pd that might be deposited in the interlayer between β-Bi2O3 and Bi2Sn2O7. The degradation mechanism of MB over Pd/β-Bi2O3–Bi2Sn2O7 in the visible region showed that the dye degradation proceeds through evolution of ˙O2− and ˙OH radicals as evaluated using photoluminescence and free radical trapping experiments. An insight into the electrical properties including the dielectric constant and impedance of the materials indicates that Pd/β-Bi2O3–Bi2Sn2O7 has the highest conductivity based on increasing the ionic transport and defects at the β-Bi2O3/Bi2Sn2O7 heterojunction. This material displayed an improved photocurrent response of a higher power conversion efficiency, exceeding that of Pt/SnO2–Bi2Sn2O7 and SnBi3 by 50% and 250%, respectively, in dye-sensitized solar cells. Picosecond-resolved photoluminescence (PL) and polarization gated PL anisotropy measurements were combined to clarify the process of FRET from the excited Pd/β-Bi2O3–Bi2Sn2O7 to SD N719. This indicates that the latter structure can be proposed as a multifunctional candidate for use in dye-sensitized solar cells, as an electrical material and as an efficient photocatalyst based on its versatile structure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...