Transport characteristics of organic solvents through carbon nanotube filled styrene butadiene rubber nanocomposites: the influence of rubber–filler interaction, the degree of reinforcement and morphology
Abstract
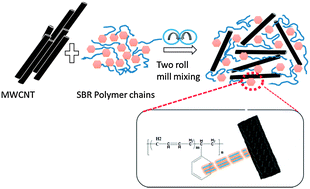
The transport behaviour of some aromatic and aliphatic solvents through carbon nanotube filled styrene butadiene rubber composites has been investigated. The aim of the present work is to investigate the role of the sorption technique in analysing the compatibility and the reinforcing effect of MWCNTs as a filler in the SBR matrix. It also focuses on the investigation of the relationship between the dispersion of CNTs in the SBR matrix and its transport behaviour. The diffusion and transport of organic solvents through the membranes have been investigated in detail as a function of CNT content, nature of solvent and temperature in the range of 28–60 °C. Solvent uptake, diffusion, sorption and permeation constants were investigated and were found to decrease with the increase of CNT loading. Transport properties could be related to the morphology of the nanocomposites. At high concentration CNT particles form a local filler–filler network in the rubber matrix. As a result, the transport of solvent molecules through the polymer is hindered. The rubber–solvent interaction parameter, enthalpy and entropy of sorption have also been estimated from the transport data. The values of rubber–solvent interaction parameters obtained from the diffusion experiments have been used to calculate the molecular mass between the crosslinks of the network polymer. The better reinforcement at higher filler loading was confirmed from the cross-link density values. The extent of reinforcement was evaluated using Kraus and Cunneen and Russel equations. The Affine and Phantom models for chemical crosslinks were used to predict the mobility of the crosslinks. The Phantom model gave better fitting indicating that the chains can move freely through one another, i.e. the junction points fluctuate over time around their mean position without any hindrance from the neighbouring molecule. The diffusivity datas of the systems have shown dependence on the temperature and microstructure of the nanocomposite. Finally, the diffusion data have been compared with theoretical predictions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...