Coaxial Zn2GeO4@carbon nanowires directly grown on Cu foils as high-performance anodes for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
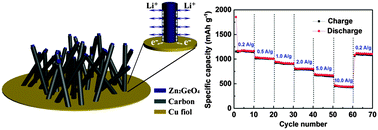
A single-step chemical vapor deposition method is utilized to prepare a novel electrode structure composed of coaxial Zn2GeO4@carbon nanowires directly grown on a Cu foil current-collector (ZGO@C/Cu), and the obtained ZGO@C/Cu hybrid electrode is employed as additive-free anode in lithium ion battery studies. The ZGO@C/Cu electrode exhibits a high reversible capacity of 1162 mA h g−1 between 0.01 and 3.0 V at a current density of 0.2 A g−1. It also shows a remarkable cycling stability and an excellent high-rate capability. At a current density of 2.0 A g−1, a stable capacity of 790 mA h g−1 is obtained without any noticeable decay over 100 cycles. Even at a high current density of 10 A g−1, a reversible capacity of 465 mA h g−1 is still obtained. The synthesis approach developed here could be utilized for the fabrication of other high-performance heterogeneous electrode structures for lithium ion battery applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...