Surface enhanced vibrational spectroscopy and first-principles study of l-cysteine adsorption on noble trimetallic Au/Pt@Rh clusters†
Abstract
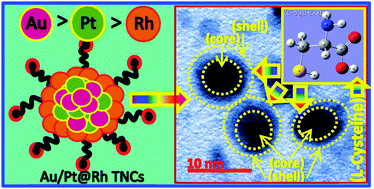
The Rh shell of the Au/Pt/Rh trimetallic nanoparticles induces a wide variety of interesting surface reactions by allowing the adsorption of amino acids like L-cysteine (L-Cys). We present a snapshot of theoretical and experimental investigation of L-Cys adsorption on the surface of noble trimetallic Au/Pt@Rh colloidal nanocomposites. Density functional theoretical (DFT) investigations of L-Cys interaction with the Rhodium (Rh) shell of a trimetallic Au/Pt@Rh cluster in terms of geometry, binding energy (EB), binding site, energy gap (Eg), electronic and spectral properties have been performed. L-Cys establishes a strong interaction with the Rh shell. It binds to Rh by the S1-site, which makes a stable L-Cys–Rh surface complex. DFT can be taken as a valuable tool to assign the vibrational spectra of the adsorption of L-Cys on trimetallic Au/Pt@Rh colloidal nanocomposites and mono-metallic Rh nanoparticles. Surface-enhanced infrared spectroscopy (SEIRS) with L-Cys on a Rh6 cluster surface has been simulated for the first time. Experimental information on the L-Cys–Rh surface complex is included to examine the interaction. The experimental spectral observations are in good agreement with the simulated DFT results. Characterization of the synthesized trimetallic Au/Pt@Rh colloidal nanocomposites has been done by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) with selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements, zeta potential, zeta deviation analysis and UV-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopic studies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Surface-enhanced spectroscopies

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...