Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core–shell structure
Abstract
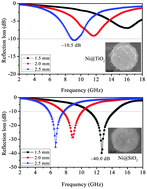
In this work, amorphous TiO2 and SiO2-coated Ni composite microspheres were successfully prepared by a two-step method. The phase purity, morphology, and structure of composite microspheres are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Due to the presence of the insulator SiO2 shell, the core–shell Ni–SiO2 composite microspheres exhibit better antioxidation capability than that of pure Ni microspheres. The core–shell Ni–SiO2 composite microspheres show the best microwave absorption properties than those of pure Ni microspheres and Ni–TiO2 composites. For Ni–SiO2 composite microspheres, an optimal reflection loss (RL) as low as −40.0 dB (99.99% absorption) was observed at 12.6 GHz with an absorber thickness of only 1.5 mm. The effective absorption (below −10 dB, 90% microwave absorption) bandwidth can be adjusted between 3.1 GHz and 14.4 GHz by tuning the absorber thickness in the range of 1.5–4.5 mm. The excellent microwave absorption abilities of Ni–SiO2 composite microspheres are attributed to a higher attenuation constant, Debye relaxation, interface polarization of the core–shell structure and synergistic effects between high dielectric loss and high magnetic loss.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...