Magnetic and geometric anisotropy in particle-crosslinked ferrohydrogels
Abstract
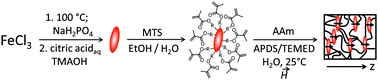
Particle-crosslinked polymer composites and gels have recently been shown to possess novel or improved properties due to a covalent particle–matrix interaction. We employ spindle-like hematite particles as exclusive crosslinkers in poly(acrylamide) gels, and exploit their extraordinary magnetic properties for the realization of ferrohydrogels with a perpendicular orientation of the preferred magnetic and geometric axes of the particles. The angle-dependent magnetic properties of uniaxially oriented gels are investigated and interpreted with respect to particle–matrix interactions. The impact of the particle orientation on the resulting angle-dependent magnetic performance reveals the presence of two different contributions to the magnetization: a hysteretic component ascribed to immobilized particles, and a pseudo-superparamagnetic, non-hysteretic component due to residual particle mobility. Furthermore, a plastic reorientation of magnetic particles in the matrix when subjected to a transversal field component is observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...