Hidden aspects of the Structural theory of chemistry: MC-QTAIM analysis reveals “alchemical” transformation from a triatomic to a diatomic structure†
Abstract
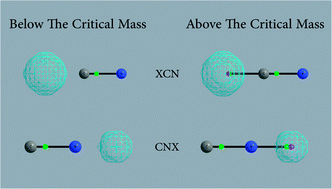
The Structural theory of chemistry introduces chemical/molecular structure as a combination of relative arrangement and bonding patterns of atoms in a molecule. Nowadays, the structure of atoms in molecules is derived from the topological analysis of the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM). In this context, a molecular structure is varied by large geometrical variations and concomitant reorganization of electronic structure that usually take place in chemical reactions or under extreme hydrostatic pressure. In this report, a new mode of structural variation is introduced within the context of the newly proposed multi-component QTAIM (MC-QTAIM) that originates from the mass variation of nuclei. Accordingly, XCN and CNX series of species are introduced where X stands for a quantum particle with a unit of positive charge and a variable mass that is varied in discrete steps between the mass of a proton and a positron. Ab initio non-Born–Oppenheimer (non-BO) calculations are done on both series of species and the resulting non-BO wavefunctions are used for the MC-QTAIM analysis, revealing a triatomic structure for the proton mass and a diatomic structure for the positron mass. In both series of species, a critical mass between that of proton and positron mass is discovered where the transition from triatomic to diatomic structure takes place. This abrupt structural transformation has a topological nature resembling the usual phase transitions in thermodynamics. The discovered mass-induced structural transformation is a hidden aspect of the Structural theory which is revealed only beyond the BO paradigm, when nuclei are treated as quantum waves instead of clamped point charges.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...