Optical properties and electronic transitions of DNA oligonucleotides as a function of composition and stacking sequence
Abstract
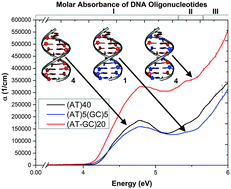
The role of base pair composition and stacking sequence in the optical properties and electronic transitions of DNA is of fundamental interest. We present and compare the optical properties of DNA oligonucleotides (AT)10, (AT)5(GC)5, and (AT-GC)5 using both ab initio methods and UV-vis molar absorbance measurements. Our data indicate a strong dependence of both the position and intensity of UV absorbance features on oligonucleotide composition and stacking sequence. The partial densities of states for each oligonucleotide indicate that the valence band edge arises from a feature associated with the PO43− complex anion, and the conduction band edge arises from anti-bonding states in DNA base pairs. The results show a strong correspondence between the ab initio and experimentally determined optical properties. These results highlight the benefit of full spectral analysis of DNA, as opposed to reductive methods that consider only the 260 nm absorbance (A260) or simple purity ratios, such as A260/A230 or A260/A280, and suggest that the slope of the absorption edge onset may provide a useful metric for the degree of base pair stacking in DNA. These insights may prove useful for applications in biology, bioelectronics, and mesoscale self-assembly.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...