Isolation of a Lewis base stabilized parent phosphenium (PH2+) and related species†
Abstract
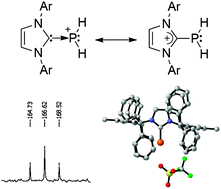
The parent phosphenium ion (PH2+), and even any phosphenium salts bearing a hydrogen (HRP+), have never been observed. The addition of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and carbon electrophiles to an NHC–PH adduct, featuring a very bulky NHC, allows for the preparation and isolation of such compounds. Computational investigations show that most of the positive charge is localized at phosphorus, demonstrating the phosphenium nature of this compound. Further, the PH moiety is able to utilize one or both of its lone pairs to bind to one or two metals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...