Affinity-mediated capture and release of amphiphilic copolymers for controlling antimicrobial activity†
Abstract
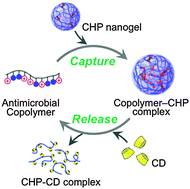
Capture and release of amphiphilic copolymers by a nano-sized polysaccharide gel (nanogel) was controlled by altering the hydrophobic binding affinity between the copolymer chains and nanogel. The antimicrobial activity of captured copolymer chains was suppressed, and regained upon release from the nanogel.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...