High interfacial lithium storage capability of hollow porous Mn2O3 nanostructures obtained from carbonate precursors†
Abstract
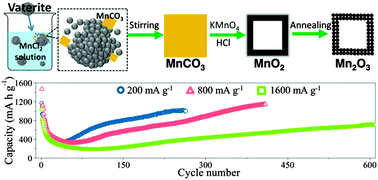
The preparation of porous Mn2O3 boxes has been developed via a carbonate precursor route. As a Li-ion battery anode, it delivers a high reversible capacity of 1442 mA h g−1 over 600 cycles at 800 mA g−1, and 65% of the capacity originates from the gradually emerging interfacial storage contribution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...