Agglutination of single catalyst particles during fluid catalytic cracking as observed by X-ray nanotomography†
Abstract
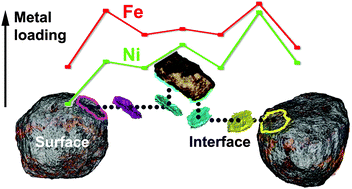
Metal accumulation at the catalyst particle surface plays a role in particle agglutination during fluid catalytic cracking.
* Corresponding authors
a
Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis group, Debye Institute for Nanomaterials Science, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands
E-mail:
b.m.weckhuysen@uu.nl
b Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, Stanford University, Menlo Park, CA, USA
Metal accumulation at the catalyst particle surface plays a role in particle agglutination during fluid catalytic cracking.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
F. Meirer, S. Kalirai, J. N. Weker, Y. Liu, J. C. Andrews and B. M. Weckhuysen, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 8097 DOI: 10.1039/C5CC00401B
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence. You can use material from this article in other publications, without requesting further permission from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given and it is not used for commercial purposes.
To request permission to reproduce material from this article in a commercial publication, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party commercial publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
