The 9-homocubyl cation rearrangement revisited†
Abstract
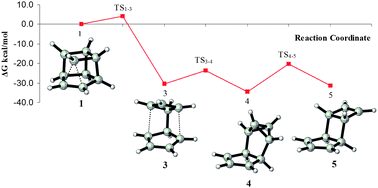
Complexity of the potential energy surface of the 9-homocubyl cation is revealed by Born–Oppenheimer molecular dynamics simulations and high ab initio levels. The stereospecific automerizations observed experimentally involve bridged ions, which have either an aromatic or an anti-aromatic character. New pathways leading to more stable isomers are unveiled.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...